UV Curing vs. Thermal Drying
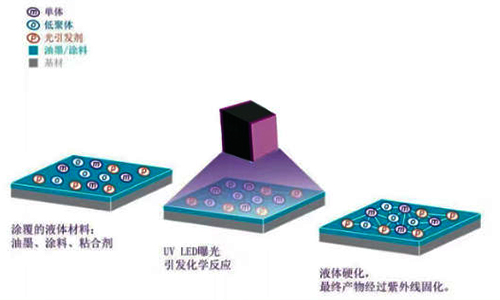
In the world of industrial manufacturing, perfectly transforming liquid materials into solid, durable surface coatings or ink layers is a critical step. In this race to "turn liquid into solid," thermal drying and ultraviolet (UV) curing technologies are two main contenders. While they share the same goal, their paths and inherent characteristics are completely different. Understanding their core differences is key to choosing the best solution for your specific application.
1. How They Work: The Fundamental Difference Between Thermal Evaporation and Photochemical Polymerization
Thermal drying is a physico-chemical process reliant on heat energy. It uses equipment like gas ovens, electric heaters, or infrared lamps to apply high temperatures to a substrate coated with ink or paint. Heat primarily plays two roles: firstly, it accelerates the evaporation of solvents or water; secondly, it provides the energy needed for thermosetting resins (like epoxy, polyester) to undergo a cross-linking reaction. This process often requires a long time (minutes to hours), and a significant amount of energy is consumed heating the surrounding air and the substrate itself.
In contrast, UV curing is an extremely fast photochemical process. Its secret lies in using specially formulated UV-curable resins that contain a key component called a "photoinitiator." When exposed to ultraviolet light of a specific wavelength, the photoinitiator instantly absorbs the light energy, generating reactive free radicals or cations. This acts like pulling a trigger, initiating a chain polymerization reaction among the monomers and oligomers in the resin, rapidly forming a strong three-dimensional polymer network. This process is completed in seconds or even fractions of a second, with energy almost entirely dedicated to the curing reaction itself, making it highly efficient.
2. Core Advantage Comparison: Efficiency, Performance, and Applicability
1. Energy Efficiency & Production Speed: UV Has a Clear Advantage
The energy consumption of UV curing technology is typically only 10%-20% of that of thermal drying. This is thanks to its precise energy delivery method—UV light acts directly on the coating instead of heating the entire workpiece and workshop environment. More importantly, its lightning-fast curing speeds (0.1-10 seconds) boost production pace by orders of magnitude, making it ideal for high-speed assembly lines and significantly reducing unit costs while increasing capacity.
2. Finished Product Quality & Performance: Each Has Its Strengths
Due to its reaction mechanism, UV curing forms a polymer network with a higher cross-link density. This typically gives UV coatings superior performance: greater hardness, stronger abrasion resistance, excellent chemical resistance (against solvents, cleaning agents), and better appearance. These properties make it the ideal choice for high-end electronics, automotive trim, and high-quality packaging applications.
Thermal drying technology, on the other hand, is better suited for handling parts with complex shapes and thicker coatings. Heat can reach shadow areas inaccessible to UV light and penetrate thicker films through convection and conduction, ensuring uniform drying. Furthermore, it is a necessary and well-established choice for traditional coating systems that lack photoinitiators (like conventional paints, powder coatings).
3. Materials and Equipment Considerations
UV curing requires the use of dedicated, photoinitiator-containing coatings, making the selection more specific. It also requires precise matching of the UV lamp's wavelength, energy, and peak irradiance, along with regular maintenance to ensure effective curing. Thermal drying has broader compatibility with coating formulas but requires large ovens and ventilation systems, resulting in a larger equipment footprint.
3. How to Choose: Guidance for Your Application
Your choice should ultimately be based on specific application needs, production goals, and budget.
Choose UV Curing when your priorities are:
Maximum production speed and lower energy costs.
The substrate is a heat-sensitive material (e.g., plastic, wood, electronics) that cannot withstand high temperatures.
There are extremely high requirements for the product surface's hardness, wear resistance, and chemical resistance.
Production line space is limited, and long ovens cannot be accommodated.
Choose Thermal Drying when your application is better suited for:
Processing three-dimensional objects or parts with complex structures that create light shadows.
The coating is very thick and requires energy to be conducted evenly from the inside out.
The coating system used is traditional (e.g., solvent-based paints, powder coatings) and there are no plans to change the formula.
Initial investment budget is a primary concern, as the upfront cost of thermal drying equipment may be lower than a high-end UV system.
In summary, UV curing, with its high efficiency, energy savings, and high performance, represents the future trend of modern manufacturing, especially in high-speed, high-quality production scenarios where it is irreplaceable. Thermal drying, as a mature and reliable technology, still firmly holds an indispensable position in specific areas involving complex parts. A deep understanding of the principles and differences between the two will help you make the smartest and most economical technology decision.
 HOT LINE: 086-577-65159218
HOT LINE: 086-577-65159218












