UV Hot Melt Pressure Sensitive Adhesives: The Future - Production Processes and Applications
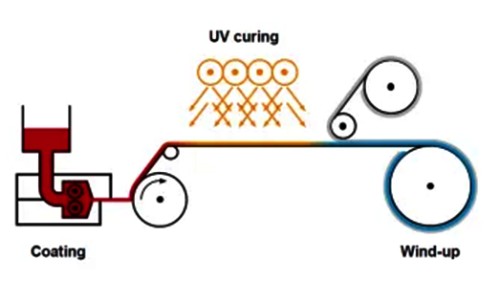
Compared to traditional oil-based or water-based adhesive coating, UV Hot Melt Adhesive has very high viscosity. It requires a heated suction cup to dip into the adhesive tank, draw in the adhesive, and transport it through pipes to the hot melt extrusion coating head. Coating occurs at approximately 100°C onto the substrate. The coated material is then conveyed into a UV oven for cross-linking and curing, before finally being wound up. Apart from the coating method and curing mechanism, the process is essentially similar to traditional methods. Of course, specialized coating production equipment is still required.
Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs) are soft polymeric materials that possess persistent tackiness at room temperature. They adhere to surfaces under light pressure via non-covalent bonds and can be peeled off without leaving residue. Due to their characteristics of easy adhesion, persistent tack, clean removability, and reusability, they are widely used in automotive, electronics, medical, and industrial fields.
The main types of PSAs commonly used today are rubber-based PSAs, acrylic PSAs, and silicone PSAs.
UV Curing for PSA Production
Using UV curing to produce PSAs involves coating solvent-free liquid components onto a substrate, followed by UV irradiation for photopolymerization. This eliminates the need for thermal drying ovens, simplifies the production line, is environmentally friendly with near-zero emissions, and significantly improves production efficiency.
Radiation-curable (UV-curable) PSAs combine the advantages of environmental friendliness and energy efficiency. They avoid the high pollution associated with solvent-based PSAs and the defects of poor aging resistance and high-temperature performance found in hot melt PSAs.
Types of UV PSAs
1. UV Hot Melt PSA (HMUV PSA)
Hot melt coated UV-curable PSAs typically use relatively high molecular weight polyacrylates as the base polymer. They possess high bulk viscosity and require heating to around 100°C for coating. Benzophenone derivative photoinitiators are often grafted onto the polymer backbone, ensuring uniform distribution and low residual odor. After UV curing and cross-linking, the adhesive layer exhibits excellent cohesive strength and temperature resistance. They can fully replace solvent-based adhesives for high-end applications such as:
They outperform water-based PSAs in low-temperature performance and water whitening resistance. Their weather resistance and aging resistance are unmatched by conventional hot melt adhesives. Therefore, hot melt UV-curable PSAs represent the mainstream direction of development.
Regarding coating equipment investment, the price of high-precision imported coating heads has now fallen below 1 million yuan. Overall machine investment costs have also decreased significantly, amounting to less than 1/30th of the cost of imported water-based coating lines. Furthermore, they offer low energy consumption, small footprint, and no wastewater pollution. They represent the future direction for PSA development.
2. Room Temperature (RT) Coatable UV PSA
Examples of RT coatable PSAs include:
Solutions of thermoplastic elastomers in acrylic monomers
Solutions of acrylated acrylic polymers in acrylic monomers
Solutions of acrylated polyurethanes in acrylic monomers.
When irradiated with UV light in the presence of a photoinitiator, the acrylic monomers react to form polymers, becoming an integral part of the adhesive. Common reactive diluents are 2-Ethylhexyl Acrylate, Ethoxylated Nonylphenol Acrylate, and Ethoxylated Ethyl Acrylate.
Features:
Disadvantages: Compared to water-based and hot melt systems, UV monomer resins have a stronger odor, are more irritating, and can easily cause allergic reactions. Their performance under high and low temperatures, as well as compatibility across temperature ranges, is poor; tack decreases sharply in low-temperature environments. Long-term removable performance across various substrates is generally not optimal.
Adjustment Method 1: If equipment precision is insufficient or coating thickness remains fixed, specialized diluents can be added to adjust the effective solids content of the adhesive. This reduces the initial tack after drying, improving removability to some extent.
Adjustment Method 2: By optimizing the photoinitiator system and UV exposure time, the effective cure rate of the adhesive is increased, leading to better cohesive strength. This also significantly reduces the initial tack.
The viscosity of RT coatable UV PSAs is well-suited for screen printing.
The most common applications are in-line adhesive coating and printing for producing nameplates and decals.
Currently, these products have gained a degree of market adoption, particularly in the following industries:
Automotive: Wire harness tapes
Construction: Waterproofing tapes
Medical: Bandages (e.g., medical bandages)
Food: Packaging labels.
 HOT LINE: 086-577-65159218
HOT LINE: 086-577-65159218












